AC vs DC Electricity for Solar Energy

Written by: Briain Kelly
Published: November 30, 2023
Last updated: October 9, 2025
Reading time: 2 mins
Photovoltaic solar panels are becoming an increasingly popular way to power homes and businesses across Ireland.
They work by converting the limitless energy from the sun into electricity which can be used to power household appliances, thus reducing energy bills while making a positive contribution to the environment.
If you are one of those who is thinking about installing solar PV panels on your home, you may have come across the terms AC electricity and DC electricity. But what exactly do these terms mean, how do they differ, and why do they matter?

What is AC electricity?
Alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical current which is used primarily in power transmission and household appliances.
This type of electrical current sometimes changes direction and magnitude continuously with time, in contrast with DC electricity, which flows only in one direction.
AC current is what is primarily used to power household and business appliances, such as kitchen appliances, televisions, electric lamps and fans, through an AC wall socket.
AC electricity can be easily converted to different voltages using transformers and is more suited to long-distance transmission, as power loss is reduced.
In the case of solar panels, DC electricity is converted into AC electricity, which can be used to power household appliances.
AC is also used to transmit information, such as is the case with telephones and cable television.

What is DC electricity?
Direct current (DC), in contrast to AC, flows only in one direction. DC can flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors and insulators.
Direct current electricity is commonly found in PV solar panels, electronic devices like phones and laptops, electric vehicles, batteries, and other applications where a stable, single direction current is needed.
In a solar panel system, DC electricity is produced inside a solar cell when a photon knocks an electron free from its bond.
Positively charged electrons are then free to move in a single direction inside the silicon cells.
This direct current is must then be converted into alternating current via an inverter.
What electricity is produced by solar panels?
A solar inverter converts direct current electricity produced in solar cells into alternating current electricity, which can be used in homes and businesses.
Direct current is well-suited for photovoltaic solar panels for a number of reasons, the first being that it is the type of electricity naturally produced through the photovoltaic effect.
Many solar components, such as inverters and charge controllers, operate on direct current.
DC electricity is also commonly used to charge batteries, which are integral to many solar power systems for energy storage. Batteries store and release energy in a DC form, which can then be converted to AC electricity.
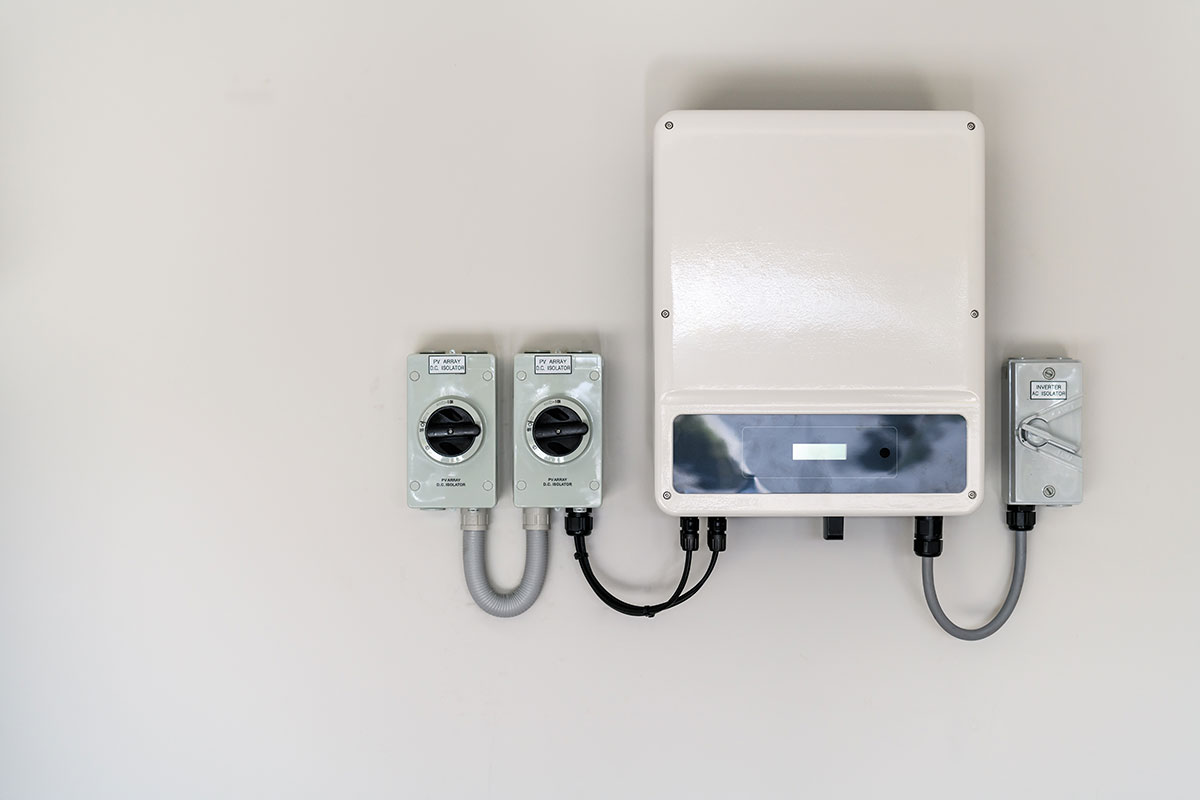

How to convert DC to AC Electricity
Direct current (DC), in contrast to AC, flows only in one direction. DC can flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors and insulators.
Direct current electricity is commonly found in PV solar panels, electronic devices like phones and laptops, electric vehicles, batteries, and other applications where a stable, single direction current is needed.
In a solar panel system, DC electricity is produced inside a solar cell when a photon knocks an electron free from its bond.
Positively charged electrons are then free to move in a single direction inside the silicon cells.
This direct current is must then be converted into alternating current via an inverter.
Get a Quote
Now that you know the difference between AC and DC electricity, and how they are used differently, why not take the first step on your solar journey by getting a quote from a trusted installer in your area – 100% free of charge.
Speak with the experts at Energy Efficiency today for the best quotes on the market.
AC vs DC Electricity for Solar Energy
Published: November 30, 2023
Last updated: October 9, 2025

Written by: Briain Kelly
Reading time: 2mins
Photovoltaic solar panels are becoming an increasingly popular way to power homes and businesses across Ireland.
They work by converting the limitless energy from the sun into electricity which can be used to power household appliances, thus reducing energy bills while making a positive contribution to the environment.
If you are one of those who is thinking about installing solar PV panels on your home, you may have come across the terms AC electricity and DC electricity. But what exactly do these terms mean, how do they differ, and why do they matter?

What is AC electricity?
Alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical current which is used primarily in power transmission and household appliances.
This type of electrical current sometimes changes direction and magnitude continuously with time, in contrast with DC electricity, which flows only in one direction.
AC current is what is primarily used to power household and business appliances, such as kitchen appliances, televisions, electric lamps and fans, through an AC wall socket.
AC electricity can be easily converted to different voltages using transformers and is more suited to long-distance transmission, as power loss is reduced.
In the case of solar panels, DC electricity is converted into AC electricity, which can be used to power household appliances.
AC is also used to transmit information, such as is the case with telephones and cable television.

What is DC electricity?
Direct current (DC), in contrast to AC, flows only in one direction. DC can flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors and insulators.
Direct current electricity is commonly found in PV solar panels, electronic devices like phones and laptops, electric vehicles, batteries, and other applications where a stable, single direction current is needed.
In a solar panel system, DC electricity is produced inside a solar cell when a photon knocks an electron free from its bond.
Positively charged electrons are then free to move in a single direction inside the silicon cells.
This direct current is must then be converted into alternating current via an inverter.
What electricity is produced by solar panels?
A solar inverter converts direct current electricity produced in solar cells into alternating current electricity, which can be used in homes and businesses.
Direct current is well-suited for photovoltaic solar panels for a number of reasons, the first being that it is the type of electricity naturally produced through the photovoltaic effect.
Many solar components, such as inverters and charge controllers, operate on direct current.
DC electricity is also commonly used to charge batteries, which are integral to many solar power systems for energy storage. Batteries store and release energy in a DC form, which can then be converted to AC electricity.

How to convert DC to AC Electricity
Direct current (DC), in contrast to AC, flows only in one direction. DC can flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors and insulators.
Direct current electricity is commonly found in PV solar panels, electronic devices like phones and laptops, electric vehicles, batteries, and other applications where a stable, single direction current is needed.
In a solar panel system, DC electricity is produced inside a solar cell when a photon knocks an electron free from its bond.
Positively charged electrons are then free to move in a single direction inside the silicon cells.
This direct current is must then be converted into alternating current via an inverter.
Get a Quote
Now that you know the difference between AC and DC electricity, and how they are used differently, why not take the first step on your solar journey by getting a quote from a trusted installer in your area – 100% free of charge.
Speak with the experts at Energy Efficiency today for the best quotes on the market.
Solar Energy Saves Households Thousands in Electricity Costs
Take our 2-minute questionnaire and find affordable solar options to suit your budget and lifestyle.