Home insulation will help keep your house warm during the cold winter months and reduce your energy bills by preventing unnecessary heat loss through the fabric of the building – and there are a number of different locations in your home where this can be prevented.
Heating oil prices fell in 2023 after two years of increases. However, there is no guarantee that they won’t rise again in the near future. Because of that, homeowners should take steps to ensure their house is properly insulated to be more energy efficient, as around a third of the heat in an uninsulated home can be lost through the walls alone.
There are multiple methods and materials which can be used to insulated the attic, walls, and floors of any home. Choosing the best method or combination of methods will vary from home to home.
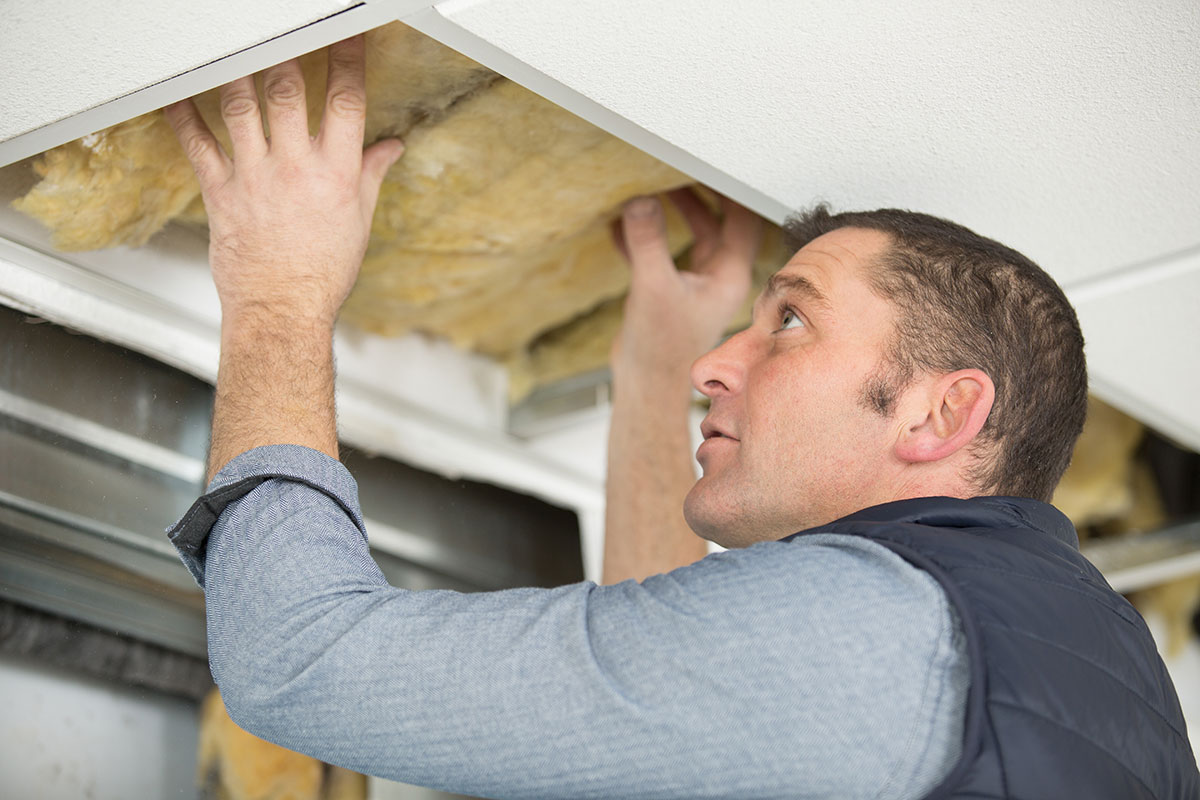

Table of Content
What is the best way to insulate your home?
There are a number of ways of insulating your home to help to prevent heat loss, including wall, attic and floor insulation. The best method of insulating your home will depend on your own unique circumstances, and what insulation your home already has. Most homes built in the past 20 years should already be insulated.
But for many people, their insulation is inadequate, and heat loss through the walls, floorboards and attic might be costing them hundreds per year on heating which can be reduced by improving the building’s energy efficiency.
When choosing where to begin installing insulation you should first consider what options will deliver the largest gains in the most cost effective fashion, without greatly disturbing the building. First, let’s look at the different types of home insulation that you can avail of in more detail.
Best Attic Insulation in Ireland
Advantages
The four main types of attic insulation are rolled wool attic insulation, pumped cellulose, polystyrene board, and spray foam insulation. There are considerable differences between these distinct methods on insulating an attic space, including how effective their thermal performance is.
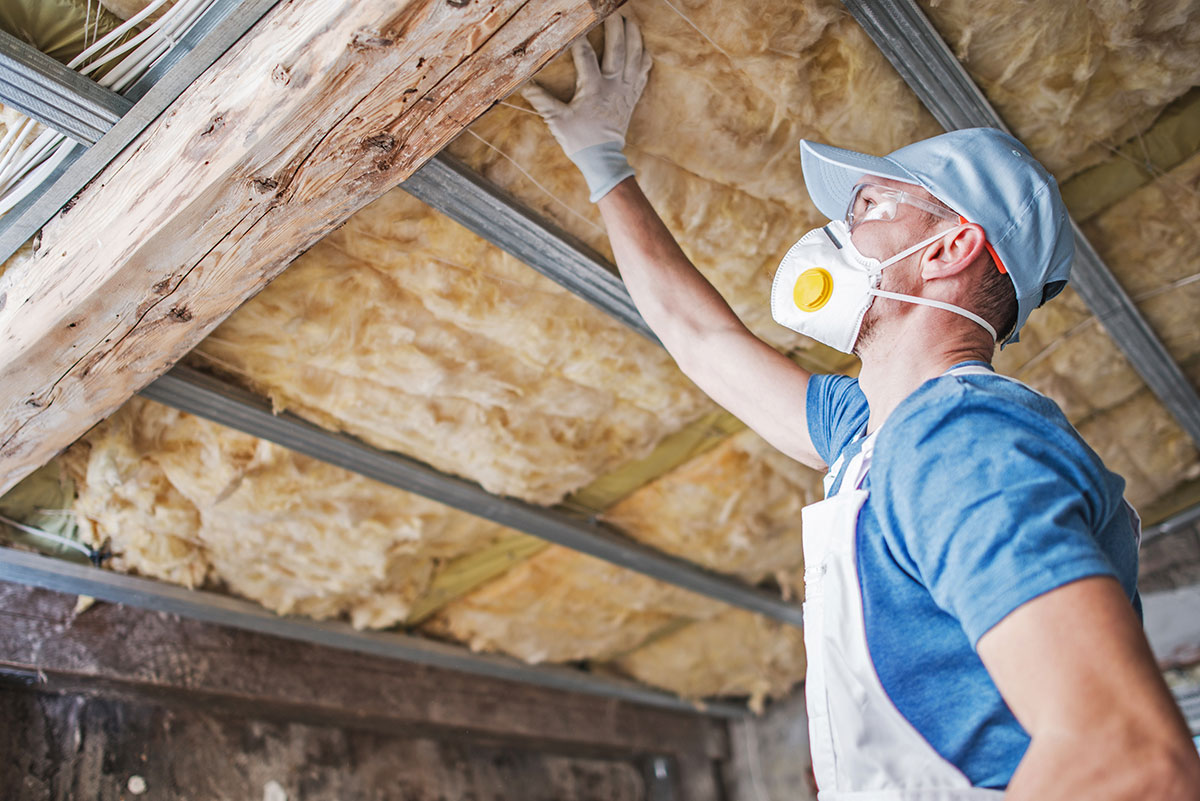

Different Ways to Insulate an Attic
There are two main ways in which attic insulation can be installed, Loft Insulation or Rafter Insulation. Which you choose will depend largely on how the attic space or might be used in the future.
Loft Insulation is the simplest way to insulate an attic. Rolls of mineral wool are laid down in perpendicular layers between the ceiling joists. This has the benefit of creating a smaller envelope of space to heat within the home. Though it will result in a cold attic.
Rafter Insulation involves either spray foam or rigid board insulation being installed between the rafters of a pitched roof building. This will create a warm void within the attic space, useful if it will be used or converted later.
Why Wall Insulation is so Important
Up to 30% of the heat in your home can be lost through the walls, and insulation can make your home more comfortable, warmer, and save money on heating bills.
Older homes, such as those constructed 90 years ago or more, have solid walls, meaning insulation cannot be placed within them to keep homes warm and must be placed on the outside or inside the wall.
Homes built in the past 50 years or so typically have cavity walls, which basically means that they have a hollow centre where insulating materials can be placed.
Insulation for Solid Walls
Solid wall insulation will typically cost more than cavity wall insulation, however the savings can be even greater. Because there is no cavity, or gap, in the wall, insulation for solid walls must be placed outside (external) or inside (internal).
External Wall Insulation
Advantages
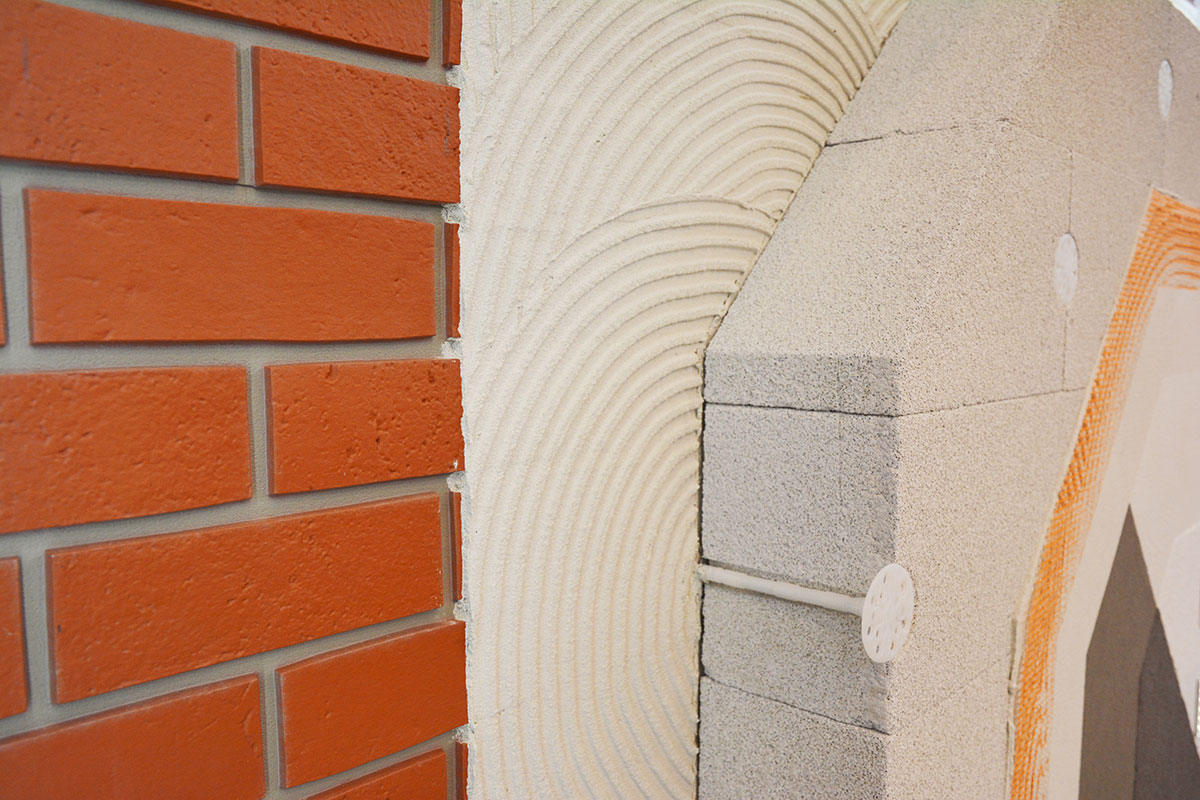
External wall insulation is the most popular way of insulating homes which were built before the 1930s with solid walls. This type of insulation is applied to the exterior of the wall instead of inside. A number of materials can be used for external wall insulation, but expanded polystyrene (EPS) is most commonly used. Phenolic boards or mineral wool can also be used for external wall insulation.

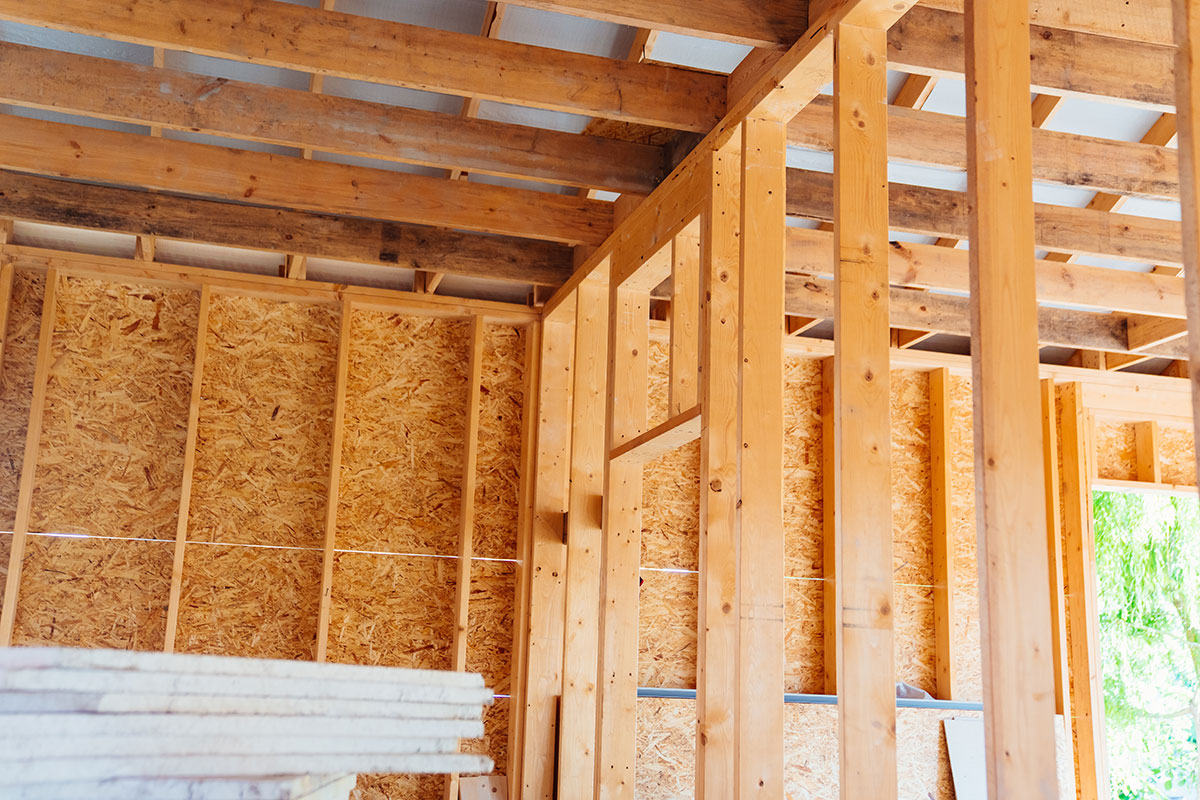
Internal Wall Insulation
Advantages
Solid walls can be insulated by fitting rigid insulation boards to the inside of the wall, or by building a stud wall filled in with insulation material.
Insulation boards are usually made from one of several forms of foamed plastic, while stud walls work are attached to the wall and filled in with mineral wool fibre.

Insulation for Cavity Walls
Insulating cavity walls offers significant savings on heating costs, making homes more energy efficient and comfortable. Cavity wall insulation differs to solid walls in that cavity walls have an inner leaf and outer leaf – meaning they have a hollow or cavity which allows for insulating materials to be placed within the wall itself as opposed to the inside or outside. Homes built from the 1980s onwards are likely to have cavity walls.
Cavity walls are commonly insulated with blown mineral fibre insulation, such as fibreglass insulation, polystyrene beads and sometimes spray foam.
How are cavity walls insulated?
In short, cavity walls are insulated by specialist installers who drill holes in the wall before injecting the insulating material through the holes and then covering the holes with cement.
Home insulation companies will send someone out to your home to drill small holes of around 22 millimetres, at intervals of around 1 metre on the outside wall of your home. The next step is to pump insulation into the cavity using special equipment before filling in the holes so that they are barely noticeable.
Floor insulation in Ireland
Advantages
The best type of insulation for your home will depend on the type of flooring that you have. Only the ground floor typically needs to be insulated, and it could cost €5,500 to have the work carried out.
Many homes have a ground floor made of solid concrete, which can be insulated if it needs to be replaced. Solid concrete can also have rigid insulation laid on top.
Older homes are more likely to have suspended timber floors, which can be uprooted to have mineral wool insulation inserted between the joists of the floor.
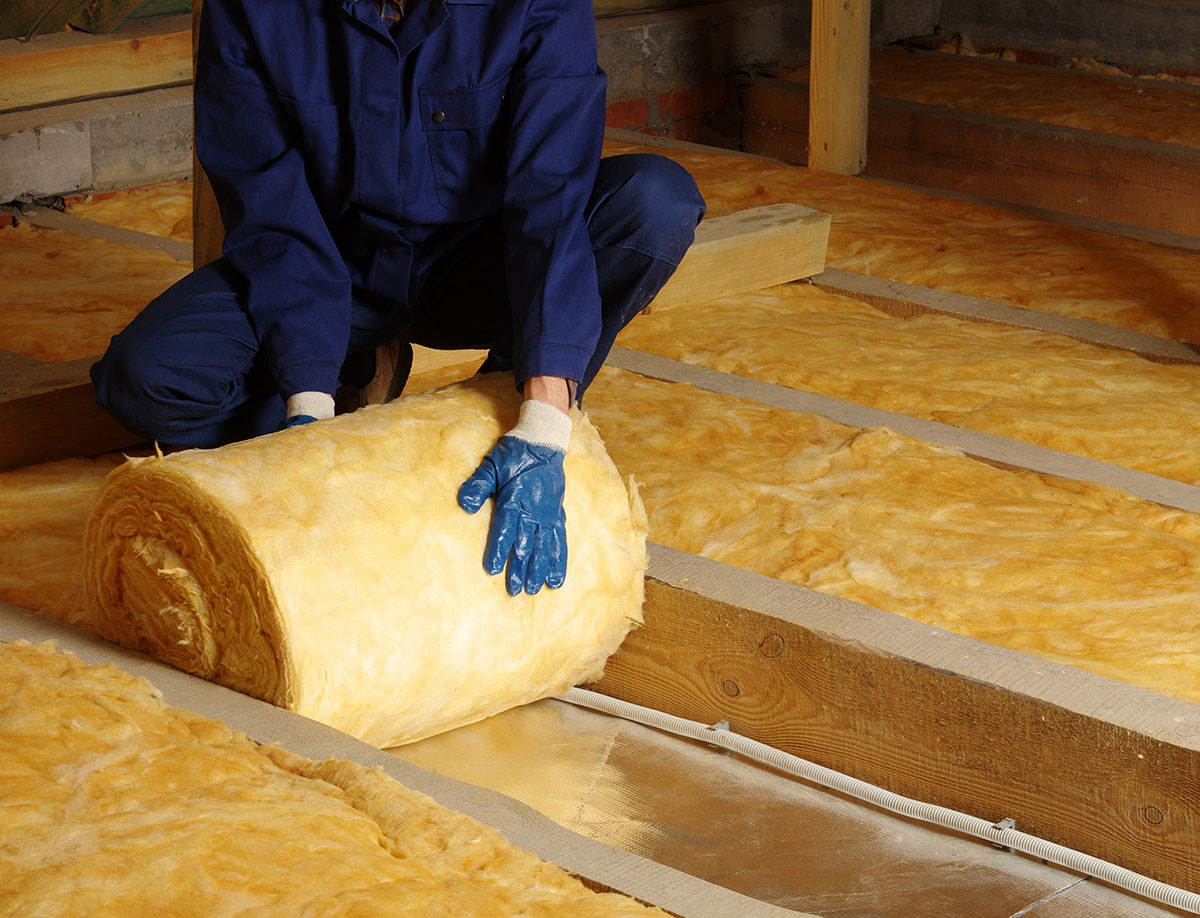

What are the best materials for home insulation?
A number of different materials can be used for home insulation. The three most common types of insulation used for homes in Ireland are fibreglass, cellulose and spray foam. The type of insulation material that is best suited to you will depend on your home, the method of insulation that you require and how much you want to spend.
Availing of a free quote is the most effective way of ensuring you choose the best home insulation method for you.
Home Insulation Grants in Ireland
Grants are available from the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland for wall and attic insulation. The SEAI grant amount will depend on the type of insulation that you wish to install and the size of your house. For instance, the grant you’ll receive if you have a detached house is significantly more than if you wish to insulate an apartment.

Better Energy Homes Scheme Grant Amounts
| Attic Insulation Grants All Apartment – €800 Mid-terrace house – €1,200 Semi-detached or end of terrace house – €1,300 Detached house – €1,500 |
| Cavity Wall Insulation Grants All Apartments – €700 Mid-terrace house – €800 Semi-detached or end of terrace house – €1,200 Detached house – €1,700 |
| Internal Wall Dry Lining Grants All Apartments – €1,500 Mid-terrace house – €2,000 Semi-detached or end of terrace house – €3,500 Detached house – €4,500 |
| External Wall Insulation Grants All Apartments – €3,000 Mid-terrace house – €3,500 Semi-detached or end of terrace house – €6,000 Detached house – €8,000 |
All homeowners whose homes were built and occupied before 2011 can apply for SEAI grant for home insulation. Funding is only be issued once per property for each type of works. Any properties which has previously availed of wall insulation through any government scheme therefore won’t qualify for further a further SEAI grant for insulation works.
The Main Benefits of Home Insulation
Home Insulation FAQs

Get a Home Insulation Quote Today
Protect your home against heat loss and save money on your heating bills by getting a FREE Quote for home insulation today by contacting us below.










