Table of Contents
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Home EV Chargers Ireland: Complete Guide, Costs, & Future-Proofing
Key Takeaways
- 1A Home EV Charger will cost between €800 and €1,600 in Ireland.
- 2A Level 2 Smart Charger can fully charge your electric car in 4-8 hours.
- 3There is a €300 SEAI grant to help with the cost of installing a Home EV Charger.
- 4An electric car can be half as cheap to run with home charging compared to petrol or diesel cars.
Costs and Financial Support: Making Home EV Charging Affordable
The price of a Home EV Charger can be significant. However, that price can be significantly reduced by a €300 SEAI grant. This cost will also be paid back many times over with access to home charging at low prices.
How much does it cost to install an electric car charger at home?
The cost of getting an EV charger installed in your home will be somewhere between €800 and €1,600.
This price range depends on three main factors:
- 1
EV Charger Model: What type of charger are you getting installed? Different charger brands can come with different power levels. This, and the number of smart features, can greatly affect the price of a charger.
- 2
Installation Costs: The cost of installing a private EV charge point electrical system, including wiring. This will vary depending on where the charger is placed.
- 3
Electrical Upgrades: Depending on your home and chosen charger, you may have to upgrade your home’s electrical system. This can include the electricity panel, installing a dedicated circuit, or switching to a three-phase power system.
A good installer must be a qualified electrician who will assess your home beforehand. They will tell you what, if any, home upgrades are required and what they will cost.
The SEAI Home EV Charger Grant
The SEAI has a €300 grant available for home EV chargers. This grant is contingent on your property and charger meeting the requirements of the SEAI.
Full Grant Details and Eligibility
Grant Level: The grant is worth €300 to all applicants, regardless of the charger chosen or the cost of the project.
Previous Grants: The property must not have previously received any grant funding for an EV Charger.
Parking Requirements: You must have off-street parking for the electric vehicle, which is directly associated with your home.
Charger Connection: The electric car charger must be able to connect back to your home.
Approved Charger: The smart charger must be on the list of those approved by the SEAI.
Certified Installer: The electrician doing the installation must be registered with Safe Electric Ireland.

Read more about grants for Home EV Chargers, Apartment Charging Networks, and Electric Vehicles.
How much does it cost to run an electric vehicle?
The Home EV Charger Installation Process in Ireland (Step-by-Step Guide)
Step 1: Apply for the SEAI Grant and Receive Your Letter of Offer
- 1
Gather Person Information: Gather the required information about your property, including its MPRN and Eircode.
- 2
Apply Online: Apply for your electric car charger grant online through the SEAI’s web portal.
- 3
Await Letter of Offer: Wait until you receive a Letter of Offer from the SEAI with the grant approval.
Step 2: Choose a Safe Electric Registered Installer
- 1
Select Installer: Choose an EV charger installer who has a good reputation and is Safe Electric registered electrical contractor with the correct certifications. This is essential if you want to receive the €300 grant.
- 2
Home Survey: The installer will survey your home to determine the best place to install the EV charger and if any upgrades are needed for your electrical system.
Step 3: Installation Day, Testing, and Handover
- 1
Mounting the Charger: The charger is mounted at the chosen location in your home.
- 2
Electrical Connection: The installer will run the required cables connecting your charger to the power supply.
- 3
Testing the Charger: Your charger will be tested and the control app set up before it is handed over to the user.
- 4
Commissioning & Handover: Once the setup is complete, the installer will explain the ins and outs to you and hand over the EV charger for use.
- 5
Claim Your Grant: The electrician will complete the Installation Details Form and provide it to you along with a copy of Certificate Number 3 and a test record sheet. These must be submitted by the homeowner along with the completed Payment Request Form.
The Different Types of Electric Car Chargers
Electric car chargers can differ greatly from one another depending on their strength, smart features, connectors, and power supply.
Before getting into the other characteristics of car chargers, the broadest way in which they are classified is as slow, rapid, or fast chargers.
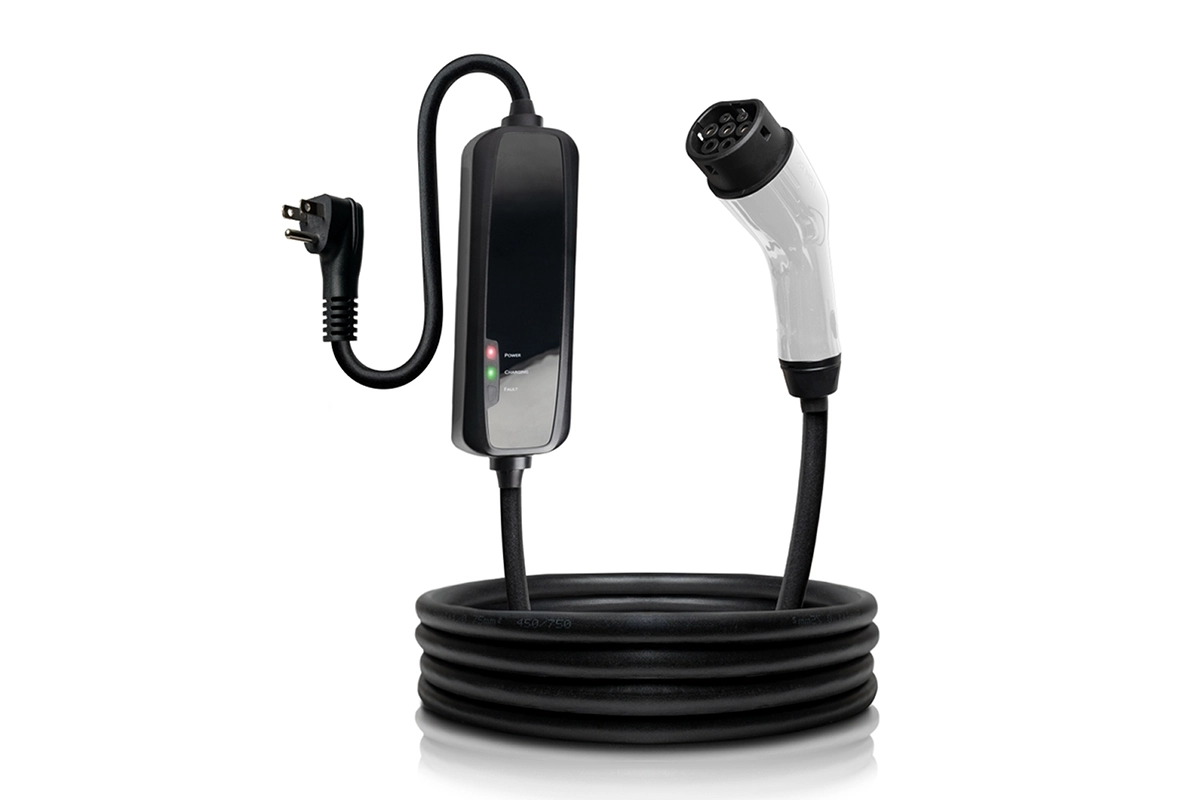

Slow
Three-pin plug chargers, also known as “granny chargers”, are called Level 1 chargers. These are basic charging cables that plug directly into a wall socket. A three-pin charger is only able to deliver 2.3kW per hour since it can only use the power supplied by the socket.

Fast
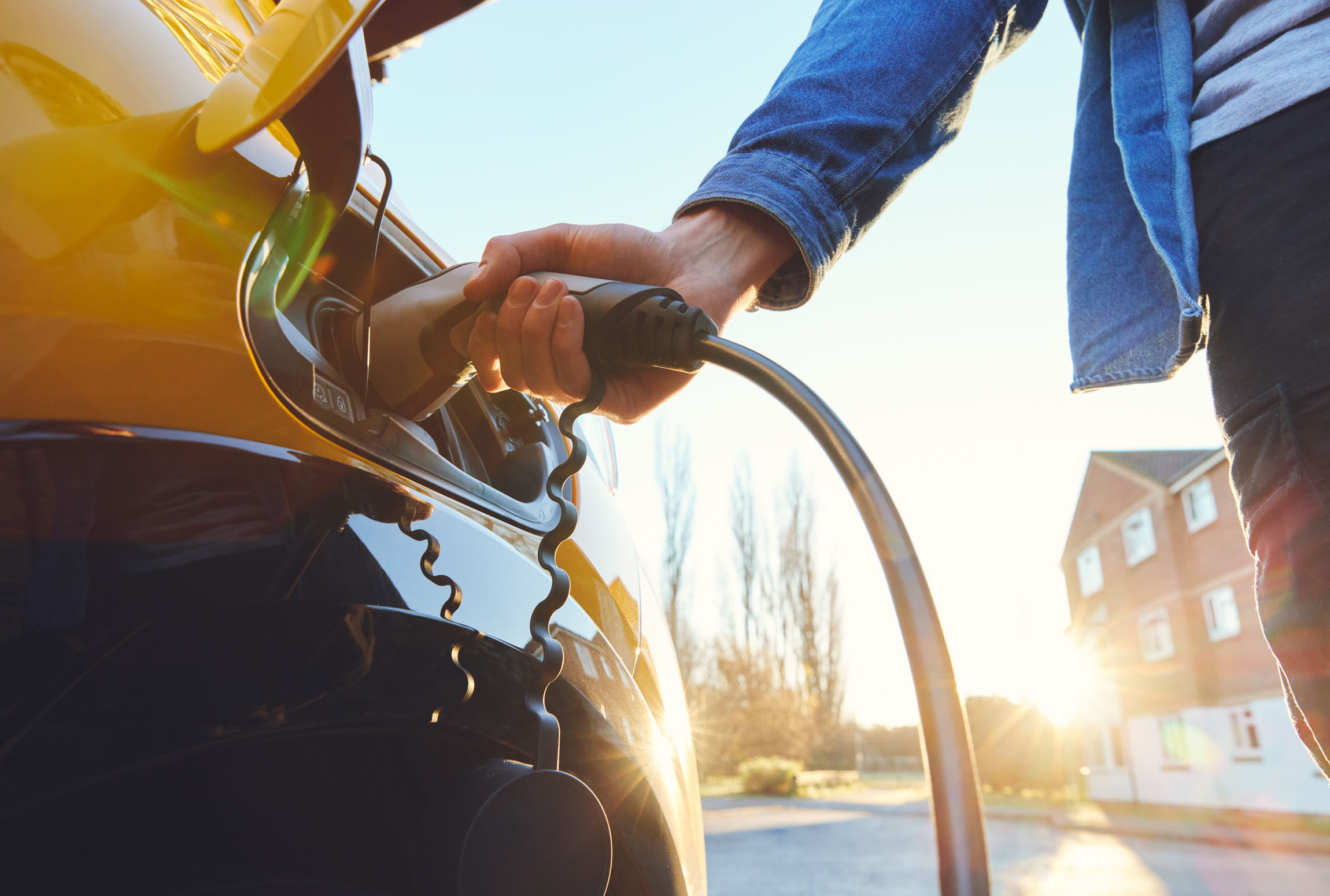
A dedicated Level 2 home EV charger with a wall-mounted box and charging cable. These have an AC charging strength of 7kW – 22kW. Most Irish homes can only run up to a 7.4kW charger on a single-phase electricity supply. A three-phase supply is needed for an 11kW to 22kW charger as they require a higher voltage.
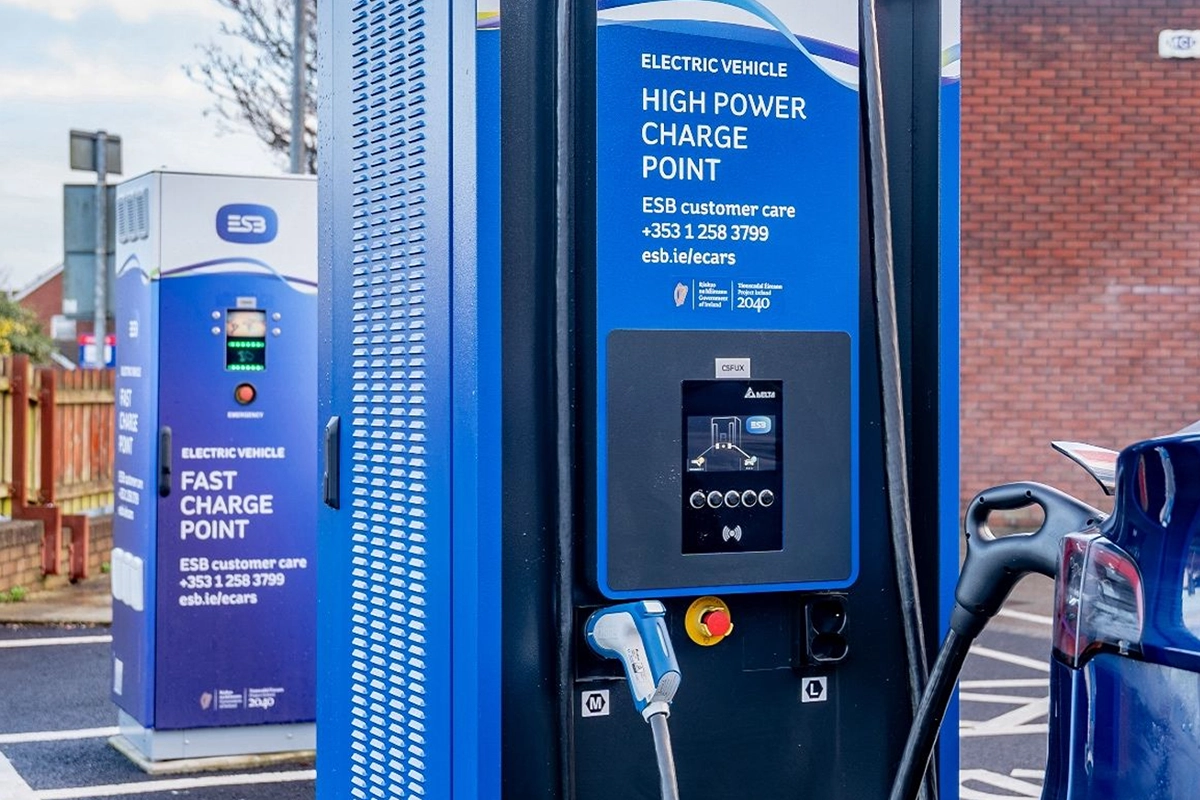

Rapid
Level 3 Rapid Chargers or High Power Chargers. These can have a strength of anywhere from 50kW to over 400kW. They are bulky, need a stronger power supply, and are usually only found in public or commercial charging stations. They are DC chargers instead of AC. This can charge faster since it isn’t limited by the car’s onboard converter.
Power Output – How Fast Can You Charge?
How fast you can charge your electric vehicle will depend on both the type of charger that you have and the size of your battery.
Granny Charger:
Only suitable for overnight charging. Can deliver a max of 23kWh in the space of 10 hours.
Level 2 Home Charger:
7kw or 11kW for most home chargers. Some are capable of up to 22kW.
Cable Choice: Attached or Separate? (Tethered vs. Untethered)
With a dedicated home EV charger, you will notice that many specify they are either tethered or untethered. This means that they either have a charging cable attached to and built into the charger (tethered) or a socket where a charging cable can be fixed (untethered).
There are advantages and disadvantages to both, depending on your circumstances.
- 1
Convenience: A tethered charger will never leave you without a charging cable in case you find yourself without one.
- 2
Connector: A tethered charger can only be used with a car whose connector matches that cable. With an untethered charger, you can attach charging cables with different connector types. This can be useful if your car is imported and has a different socket than most.
- 3
Cable Length: A tethered charger obviously has a fixed length cable. This is usually 5m to 8m. An untethered charger can use whatever length cable you provide. This could be longer or shorter than its tethered alternative.
- 4
Security: A tethered EV charger has greater cable security than an untethered option. The only place the connection could be broken is at the car side, rather than at both ends.
Running Costs and Savings
Electric vehicles are considerably cheaper to run than their petrol or diesel equivalents. This is especially true if you make good use of home charging with its inexpensive electricity prices.
The only downside is that it does take longer to charge an electric car compared to filling the tank on an ICE engine. But good charging habits can also eliminate this inconvenience.
How Long Does it Take to Charge an Electric Car at Home?
How long it takes you to charge your electric vehicle at home will vary depending on the strength of the charger, the size of your EV’s battery, and the battery’s state of charge.
- 1
Charger Strength: Home EV Chargers will vary from a maximum power of 7kW to 22kW. This means that they could add between 7kWh and 22kWh to your battery each hour when at max strength.
- 2
Battery Capacity: What is the capacity of your electric vehicle’s battery in kWh?
- 3
State of Charge: This refers to the percentage of the battery remaining at the start of a charging session, and how high you want to charge it.
With a medium-sized EV (60kW battery), a 7kW charger could charge your vehicle from 20% to 80% in under seven hours. However, charging speeds are likely to vary during a prolonged charging session.
Charging speeds also typically begin to taper off after the battery reaches 80%. That final 20% can take as long as the first 40% – 50% of a charging session.
In addition, many electric vehicles are unable to use 22kW AC charging. They will max out at 7kW or 11kW, regardless of the strength of your charger.
Comparison of Standard vs. Night-Rate EV Electricity Tariffs
Many electricity providers have cheaper rates for nighttime charging, and even special EV charging rates. The following table shows the best tariffs specifically aimed at electric vehicle charging vs standard rates.
Find the Best EV Electricity Plan
However, with the cheapest EV tariffs, what is also important is the hours of the day in which they are available.
Find the Best EV Electricity Plan
However, with the cheapest EV tariffs, what is also important is the hours of the day in which they are available.
The Benefits of Home EV Charging
Charging your electric car at home has many benefits in terms of financial savings, convenience, and always having a full battery when you need it.
Constant Availability: Your home charger is always available for you. Never waste time searching for a public charging station that’s not in use.
Full Battery: Start your commute each day with a full battery, regardless of how much you have travelled the previous day.
Time Saving: Plug your car in at home and go about your everyday life. No more waiting 30 minutes or more at a filling station for it to charge.
Range Anxiety: Spend less time worrying if you have the range left to get where you are going or reach the next charging station.
Special Discounted Rates: Electricity plans are available specifically for charging your electric car extremely cheaply.
Cheaper than Public Charging: Charging an electric car at home will always be cheaper than using public charging stations.
Low Motor Tax: By switching to an electric vehicle, you pay the lowest rate of Motor Tax in Ireland, €120 per year.
- Avoid Deep Discharge: With a constantly available car charger, you can avoid having your battery go down to 0%. This kind of deep discharge can put stress on the battery and accelerate its degradation if done repeatedly.
- Avoid Overcharging: With less range anxiety, many drivers won’t need to charge to 100% all the time. You can instead keep it topped at a healthier 80% on the regular.
- Safety Features: A proper home EV charger has many more built-in safety features than an older granny charger. These provide multi-layered electrical protection for your home and electric car.
A significant part of the cost of getting an EV charger for your home is the installation cost. This involves creating a connection point in your garage or on the exterior wall. This is then also wired to your electrical system.
Having an EV charger installed on your home can be a good selling point that will increase its value. Even if you take the charger itself with you, any new owner can easily plug a new charger into the connection point.
Safety and Efficiency (Wallbox vs. Three-Pin Plug)
Both the three-pin plug and dedicated home EV chargers are perfectly safe to use. However, a level 2 charger has the granny charger beaten in cable management and smart features that protect you and it from damage.
Level 2 Wallbox
Cable: The cable is clearly visible between the wall mounted charger and your electric vehicle at a safe height.
Load Balancing: Chargers with dynamic load balancing can adjust their power draw based on the amount of power being used in your home. This eliminates the risk of overloading your panel.
Smart Sensors: Contains protections against overloading and overheating, without automatic shut off if a fault is detected.
Three-pin Plug
Low Power Draw: The limit of 2.3kW reduces the risk of overheating from excessive power consumption.
Cable: The cable is low lying as it plugs into a socket that will likely be close to the ground.
Manual Control: You can adjust the power draw on the charger manually. Do not exceed what the socket can support, especially with the wiring and electrical panels of older homes.
Built-in Display and App Control
One of the greatest strengths of a smart charger is the ability to see its status and adjust its operations manually. Depending on the make and model, you may have one or two ways to see the status of your charger.
- 1
Built in Screen: A screen built into the body of the charger can display data related to your current charging session. You may also be able to control the session by setting targets and more.
- 2
App Controls: The more common, and more in depth, way to control an EV charger is through a dedicated app.
Your EV charger’s app will offer a wide variety of features that can make a charging session much easier.
EV Charger App Features
Schedule Charging: You can set your charger to only charge at certain times, even when plugged in. This allows you to take advantage of cheaper electricity tariffs at night.
Solar Integration: An EV charger can be integrated with home solar panels to charge only using excess solar power, or a mix of solar and grid energy.
Troubleshooting: Get alerts if anything goes wrong with your electric vehicle charger and troubleshoot the most common problems that may arise.
Real Time Monitoring: See what power your charger is delivering and the status of your car battery in real time remotely.
Data Insights: A good app should let you see how much your charger has been used, over different time periods. This can help you to get the most out of your charger by understanding when you are most likely to need a charge.
Further Guides to Home EV Charger
Home EV Charging Frequently Asked Questions
Depending on how you charge, an electric vehicle could save you €6 per 100km compared to a petrol car, or €5 compared to a diesel engine. At 14,434km driven per year, that amounts to annual savings of €721.7 (petrol) or €866.04 (diesel).
Yes, with the right charger you can charge an electric car using energy from your solar panels. The Myenergi Zappi is the preferred model of EV charger for seamless solar charging in Ireland.
It is far cheaper to use a home EV charger than a public charging station. With ESB ecars charging stations the cost to charge is between 54c and 66c per kWh. Home EV charging can be as cheap as 5c to 10c per kWh with a discounted night rate.
No, there is no direct tax deduction to buy yourself a home EV charger. However, employers who provide employees with an electric vehicle can also provide them with a car charger. There is no benefit-in-kind tax due on the EV or the charger for the employee. The cost of the charger is also tax deductible for the employer.
Yes, you can get an EV charger if you live in an apartment. But this is only if the apartment complex has dedicated off street parking for a charging network to be installed.
A smart charger refers to an EV charger with smart features that allow users to control how you charge. This can include scheduled charging times, solar charging, and more.
If you are not an experienced electrician then it is inadvisable to install your own charger. Working with the electrical panel and circuits could prove hazardous. It is safer to use an installer, and it is necessary to receive the SEAI grant.
Having a home EV charger is the best value and most reliable way to charge an electric car. Public charging stations are more expensive and might not always be available.
Assuming that your home does not need any upgrades, a qualified installer should be able to fit your EV charger in a matter of hours.
A level 2 home EV charger is much faster and more reliable than a three-pin plug charger. It also offers more flexibility in its controls that make it more than worth the cost.
Technically yes, an electric car might lose 4 or 5 percent of its battery charge a month if it is left unused. But this level of power loss is not significant enough to matter.
Yes, Level 2 chargers are built to withstand all weather conditions, meaning you shouldn’t run into any issues during the harsh winter months.






