Solar technology has come a long way in recent years, and one way that is readily apparent is in the improvement in efficiency – i.e. how much sunlight they can convert into electricity.
Efficiency is affected by a number of factors, but in Ireland solar panels on homes and businesses tend to be between 15 and 24 percent efficient.
The cost of solar panels is an important consideration, as more expensive solar panels will also typically have a higher efficiency.
Try out our handy solar panel calculator to see what type and size of solar PV system is best suited to your needs.

Table of content
Why Solar Panel Efficiency is Important
There are a number of reasons why you might opt for more or less efficient solar panels depending on financial and environmental factors.
As a rule of thumb, the more efficient solar panels are, the more expensive they are going to be. Being made of higher quality materials and design will push up the cost, so consider your budget when selecting panels.
You also need to take into consideration the amount of space you have available for your solar PV panels. Not all rooftops have a lot of space to install solar panels. If there is limited space on your roof, then high-efficiency panels are a better option for getting the most electricity out of every square metre of your solar PV system.
Solar Cell Efficiency V Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar Panels are made up of individual solar cells, and one thing you might notice is that solar cells are often shown to have a far higher efficiency than full panels.
The latest developments in solar cell efficiency have shown experimental technologies reaching as high as 47% efficiency at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in the US. But the most efficient residential solar panels on the market today top out at around 24%.
Solar panel efficiency is affected by more than just the efficiency of the solar cells. It is also determined by how those cells are arranged and connected, how many cells are in a panel, the gaps between cells, and frame thickness. Environmental conditions such as shading, temperature, and sunlight will also come into play.
Calculating Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency ratings of solar panels are calculated by dividing their Maximum Power Output in Watts by the product of its area in m² and Standard Test Condition irradiance of 1000W/m²
Efficiency (%) = Pmax (Watts) / (Area (m²) x Irradiance (1000W/m²)) x 100
Most Efficient Solar Panels By Solar Cell Type
There are multiple different types of solar panel based on their cell structure and manufacturing process, which have different levels of efficiency.
| Solar Panel Cell Type | Efficiency Range |
| N-Type Back Contact | 21% – 24% |
| N-Type HJT | 21% – 23% |
| Mono PERC | 17% – 20% |
| Poly PERC | 16% – 17% |
Beyond just the cell type, solar panels will also have different levels of efficiency based on their size, with larger panels allowing greater power output and efficiency with more cells per panel.
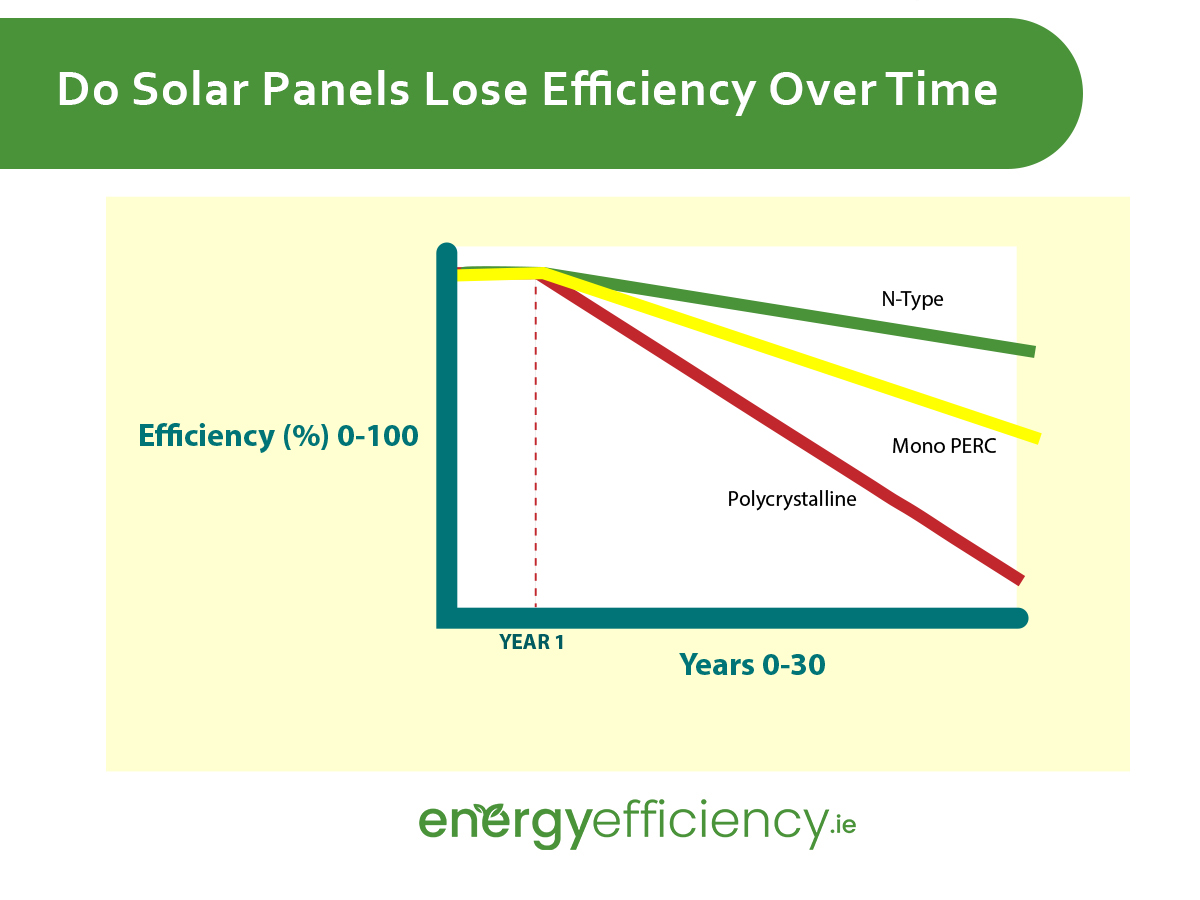
Do Solar Panels Lose Efficiency Over Time
Solar panels also degrade and lose efficiency over time, with an overall industry average rate of approximately 0.5% each year. If your solar panels are starting from a higher efficiency, then you will get much longer out of them before the loss becomes noticeable.
If you have an extremely high quality solar panel, with an annual degradation of just 0.25% efficiency, then after a 25 year period the solar efficiency will have fallen by just 6.25%.
The manufacturer’s warranty for solar panels will typically provide a guarantee of both how long the product will last, and a minimum power output guarantee after a specified length of time.
Types of Solar Panels
There are three main types of solar panels using different materials and construction methods, which deliver different levels of efficiency.
The three main varieties of solar panel technology are:
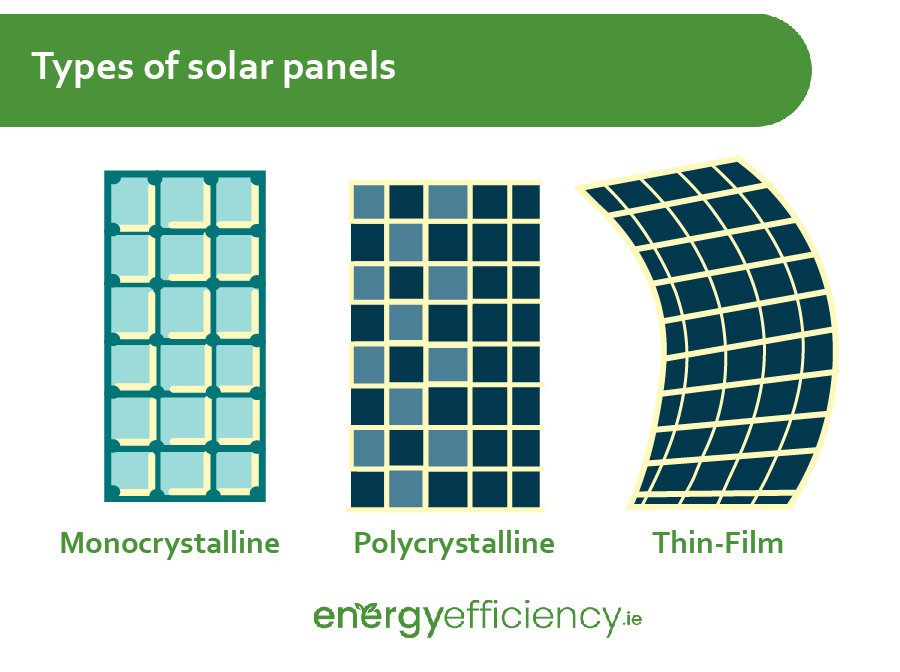
Monocrystalline Panels
The most efficient, and thus most expensive type of solar panel, monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single silicon crystal. They produce the most electricity per square metre, with an efficiency of around 17% – 24%, and thus will take up less roof space overall.
Polycrystalline Panels
Made from multiple silicon crystal fragments which are melted together, polycrystalline solar panels have a cheaper manufacturing process, making them more affordable. However this comes at the cost of lower efficiency, which usually ranges from 13% – 17%.
Thin Film Panels
Easy to produce, and flexible unlike other varieties of solar panel, Thin Film solar panels are made by layering a film of photovoltaic material over a substrate, or several layers of film. Most of these used in home installations will have an efficiency of around 6% – 15%.
There will always be examples of the cutting-edge industry leading models of each of these types of solar panel which will exceed these efficiencies. But the figures above give an approximation of most models on the market.
How Temperature Affects Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency and power output of solar panels are measured in the laboratory under what are called Standard Test Conditions. These conditions include an irradiance level of 1000w/m² and a temperature of 25°C.
Note: These conditions are for the Cell Temperature within the solar panel, which is typically 20-30°C above the ambient air temperature in the environment.
However, the temperature in real-world conditions rarely matches up with those laboratory conditions. This means that depending on what the environmental and weather conditions are like where you live, solar panels may produce more or less electricity than explicitly stated.
Solar PV systems are less effective at temperatures above their STCs, and panels can alternately operate more efficiently in lower temperatures.
The measure of how much the efficiency ratings of solar panels will be affected by temperatures above and below their STC is called the Power Temperature Coefficient, expressed as x%/°C
High-end Monocrystalline N-Type solar cell panels have a temperature coefficient -0.26% to -0.30%, meaning that for a 10-degree increase in cell temperature over 25 degrees, their efficiency will fall by 2.6% – 3%.
Older Polycrystalline, Mono PERC modules, along with Thin Film solar panels, tend to have higher Power Temperature Coefficients.
7 Years
A typical solar installation is fully paid back within 7 years. All solar panels we recommend are under warranty for 25 years, so you will enjoy at least 17 years of free energy generation.
0% VAT
As of 10 May 2023, the government has removed all VAT on solar installation and solar panel supply. This means solar has never been more affordable!
Government Grants
There is a range of government grants available for all new solar installations. Our team will guide you through the application process.
External Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
There are multiple other factors outside of the manufacturing specifications of your solar panels which will affect their real world efficiency. These can be broadly split up into environmental factors, and installation factors.
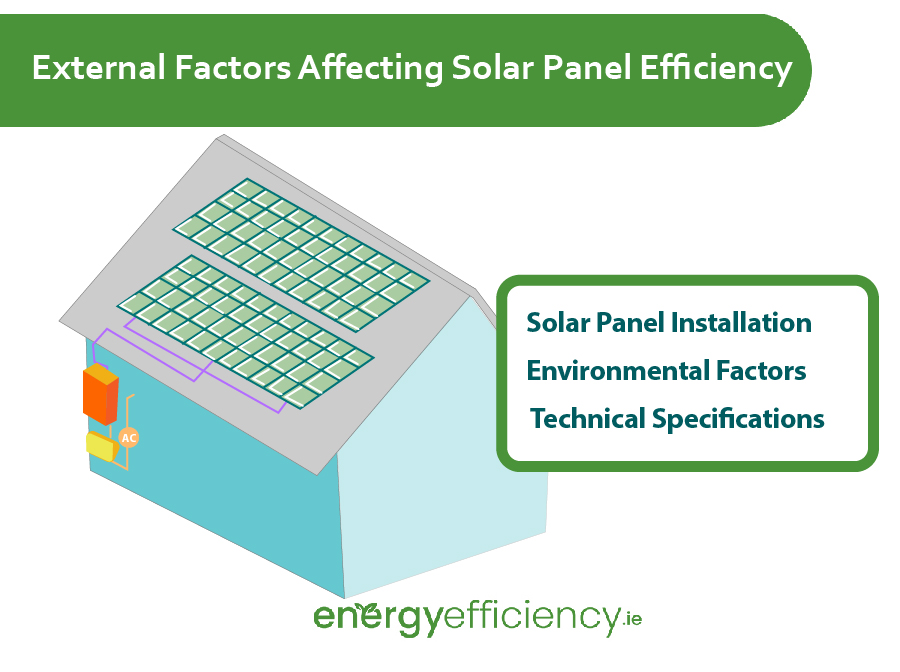
Solar Panel Installation
The location and installation of your solar panels and other elements in your solar PV system will affect how efficient they are at producing electricity.
Orientation
Solar panels should be orientated to take maximum advantage of the sun in your local environment. In Ireland, a south facing solar PV array will deliver the greatest amount of electricity overall, while east and west facing panels might also be considered depending on when you use the most electricity.
Angle
Having your solar panels installed at the correct angle is important to ensure that they absorb the most sunlight. Ideally, solar panels in Ireland should be angled at 30 – 40 degrees for the optimum absorption or sunlight.
Shading
Having your solar panels in areas where they are in shade can significantly reduce the efficiency of solar panels, or the entire array depending on your specific setup. If all of the solar panels in your PV system are connected on a string to a single inverter, then they can only operate at the level of the least efficient solar panel.
This means partial shading on just one or two panels can affect all of them. Having microinverters which are installed on each individual solar panel can help to address this issue.
Environmental Factors
Along with how your solar panels are installed, you must also take into consideration the natural elements of your area.
Hours of Sunlight
How much sunlight is received in your local area will have a profound effect on the amount of power produced by your solar panel. In Ireland, the south-east of the country receives the greatest amount of sunlight per year, while the south-west receives the least.
Temperature
Solar panel efficiency is affected by the temperature of the environment. But not in the way you might expect. The Standard Test Conditions for solar panels in the lab measure their efficiency at a cell temperature of 25 degrees Celsius. When the panel temperature rises above that level, they begin to lose efficiency.
Because the real world rarely mimics lab conditions, most solar panels specifications will include how much power they will produce under a Nominal Operating Cell Temperature (NOCT), usually around 44 degrees.
Dirt/Ice
The buildup of dirt or ice on your solar panels can severely reduce the efficiency of solar panels by blocking sunlight from getting through.
Rain
Rain itself does not affect the efficiency of your solar panels, and may actually improve their performance by keeping them clean of dirt, or cooling them off if their temperature has gotten too hot. However, rain clouds can reduce their efficiency by blocking the sunlight.
Technical Specifications Affecting Efficiency
Power Temperature Coefficient
The amount which electricity generation increases or decreases as the cell temperature rises above or below 25 degrees Celsius is known as the power temperature coefficient. The temperature coefficient is measured as a % / ℃. The lower the temperature coefficient is, the more efficient the panel is at dealing with higher temperatures.
Inverter Efficiency
The solar power inverter is what converts the DC electricity produced by your solar PV array into AC electricity which is usable in your household. Your solar panels might be connected on a string to a single inverter, or in some cases might have microinverters connected to each panel.
FAQs
Learn more about solar panels today
Take the energy efficiency online assessment today to get the best quote for your home solar panels today.
Find out how much you can save on your home energy bills with solar panels.